Configuring Environment Variables
The following environment variables need to be set in order to use the CUBRID. The necessary environment variables are automatically set when the CUBRID system is installed or can be changed, as needed, by the user.
CUBRID Environment Variables
CUBRID: The default environment variable that designates the location where the CUBRID is installed. This variable must be set accurately since all programs included in the CUBRID system uses this environment variable as reference.
CUBRID_DATABASES: The environment variable that designates the location of the databases.txt file. The CUBRID system stores the absolute path of database volumes in the $CUBRID_DATABASES/databases.txt file. See databases.txt File.
CUBRID_MSG_LANG: The environment variable that specifies usage messages and error messages in CUBRID. The initial value upon start is not defined. If it is not defined, it follows the configured locale when createdb. For more information, see Language & Charset Setting.
Note
A user of CUBRID Manager should specify CUBRID_MSG_LANG, an environment variable of DB server node into en_US to print out messages normally after running database related features. However, database related features are run normally and just the output messages are broken when CUBRID_MSG_LANG is not en_US.
To apply the changed CUBRID_MSG_LANG, CUBRID system of DB server node should be restarted(cubrid service stop, cubrid service start).
CUBRID_TMP: The environment variable that specifies the location where CUBRID for Linux stores the UNIX domain socket file. If it is not specified, the Unix domain socket file is stored in the following directory according to the process. (not used in CUBRID for Windows)
the cub_master process: under /tmp directory
the cub_broekr process: under $CUBRID/var/CUBRID_SOCK directory
the cub_javasp process: under $CUBRID/var/CUBRID_SOCK directory
Note
The CUBRID_TMP environment variable affects the java.io.tmpdir, specifying the path for temporary files created by the Java VM running in the cub_javasp process. If the CUBRID_TMP environment variable is set, the path for temporary files is designated to the path of the CUBRID_TMP environment variable, to properly store Unix domain socket files. Therefore, even if a user specifies the value of java.io.tmpdir through the java_stored_procedure_jvm_options parameter, it will be ignored. This behavior applies only to CUBRID for Linux, which supports Unix domain sockets, and not to CUBRID for Windows.
CUBRID_TMP value has some constraints, which are as follows:
Since the maximum length of the UNIX socket path is 108, when a path longer than 108 is entered in $CUBRID_TMP, an error is displayed.
$ export CUBRID_TMP=/home1/testusr/cubrid=/tmp/123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789 $ cubrid server start apricot The $CUBRID_TMP is too long. (/home1/testusr/cubrid=/tmp/123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789012345678901234567890123456789)When the relative path is entered, an error is displayed.
$ export CUBRID_TMP=./var $ cubrid server start testdb The $CUBRID_TMP should be an absolute path. (./var)
CUBRID_TMP can be used to avoid the following problems that can occur at the default path of the UNIX domain socket that CUBRID uses.
/tmp is used to store the temporary files in Linux. If the system administrator periodically and voluntarily cleans the space, the UNIX domain socket may be removed. In this case, configure $CUBRID_TMP to another path, not /tmp.
The maximum length of the UNIX socket path is 108. When the installation path of CUBRID is too long and the $CUBRID/var/CUBRID_SOCK path that store the UNIX socket path for cub_broker exceeds 108 characters, the broker cannot be executed. Therefore, the path of $CUBRID_TMP must not exceed 108 characters.
The above mentioned environment variables are set when the CUBRID is installed. However, the following commands can be used to verify the setting.
Linux
% printenv CUBRID % printenv CUBRID_DATABASES % printenv CUBRID_MSG_LANG % printenv CUBRID TMPWindows
C:\> set CUBRID
OS Environment and Java Environment Variables
PATH: In the Linux environment, the directory $CUBRID/bin, which includes a CUBRID system executable file, must be included in the PATH environment variable.
LD_LIBRARY_PATH: In the Linux environment, $CUBRID/lib and $CUBRID/cci/lib, which is the CUBRID system’s dynamic library file (libjvm.so), must be included in the LD_LIBRARY_PATH (or SHLIB_PATH or LIBPATH) environment variable.
Path: In the Windows environment, the %CUBRID%\bin and %CUBRID%\cci\bin, which is a directory that contains CUBRID system’s execution file, must be included in the Path environment variable.
JAVA_HOME: To use the Java stored procedure in the CUBRID system, the Java Virtual Machine (JVM) version 1.6 or later must be installed, and the JAVA_HOME environment variable must designate the concerned directory. See the Configuring for CUBRID Java SP Server.
JVM_PATH: To use the Java stored procedure in the CUBRD system, the JVM_PATH environment variable can specify the JVM library (libjvm) path explicitly instead of finding the library from JAVA_HOME. See the Configuring for CUBRID Java SP Server.
Configuring the Environment Variable
For Windows
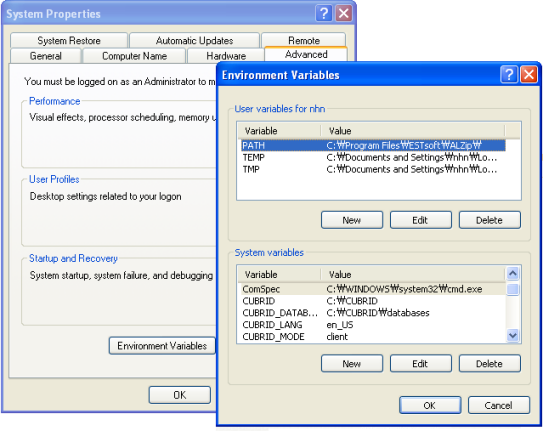
If the CUBRID system has been installed on Windows, then the installation program automatically sets the necessary environment variable. Select [Systems Properties] in [My Computer] and select the [Advanced] tab. Click the [Environment Variable] button and check the setting in the [System Variable]. The settings can be changed by clicking on the [Edit] button. See the Windows help for more information on how to change the environment variable on Windows.
For Linux
If the CUBRID system has been installed on Linux, the installation program automatically creates the .cubrid.sh or .cubrid.csh file and makes configurations so that the files are automatically called from the installation account’s shell log-in script. The following is the contents of . cubrid.sh environment variable configuration that was created in an environment that uses sh, bash, etc.
CUBRID=/home1/cub_user/CUBRID
CUBRID_DATABASES=/home1/cub_user/CUBRID/databases
ld_lib_path=`printenv LD_LIBRARY_PATH`
if [ "$ld_lib_path" = "" ]
then
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$CUBRID/lib:$CUBRID/cci/lib
else
LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$CUBRID/lib:$CUBRID/cci/lib:$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
fi
SHLIB_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
LIBPATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH
PATH=$CUBRID/bin:$CUBRID/cubridmanager:$PATH
export CUBRID
export CUBRID_DATABASES
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH
export SHLIB_PATH
export LIBPATH
export PATH
Language & Charset Setting
The language and the charset that will be used in the CUBRID DBMS is specified after the database name when DB is created(e.g. cubrid createdb testdb ko_KR.utf8). The following are examples of values that can currently be set as a language and a charset.
en_US.iso88591: English ISO-88591 encoding(.iso88591 can be omitted)
ko_KR.euckr: Korean EUC-KR encoding
ko_KR.utf8: Korean UTF-8 encoding(.utf8 can be omitted)
de_DE.utf8: German UTF-8 encoding
es_ES.utf8: Spanish UTF-8 encoding
fr_FR.utf8: French UTF-8 encoding
it_IT.utf8: Italian UTF-8 encoding
ja_JP.utf8: Japanese UTF-8 encoding
km_KH.utf8: Cambodian UTF-8 encoding
tr_TR.utf8: Turkish UTF-8 encoding(.utf8 can be omitted)
vi_VN.utf8: Vietnamese UTF-8 encoding
zh_CN.utf8: Chinese UTF-8 encoding
ro_RO.utf8: Romanian UTF-8 encoding
Language and charset setting of CUBRID affects read and write data. The language is used for messages displayed by the program.
For more details related to charset, locale and collation settings, see An Overview of Globalization.
Port Setting
If ports are closed, the ports used by CUBRID should be opened.
The following table summarizes the ports used by CUBRID. Each port on the listener that waits for connection from the opposite side should be opened.
To open the ports for a specific process on the Linux firewall, follow the guide described for the corresponding firewall program.
If available ports for Windows are used, you cannot know which port will be opened. In this case, enter “firewall” in the “Control Panel” of the Windows menu and then choose “Windows Firewall> Allow a program or functionality through Windows Firewall” and then add the program for which port should be opened.
This method can be used for the case that it is difficult to specify a specific port in Windows. This method is recommended since it is safer to add a program to the Allowed programs list than to open a port without specifying a program on the Windows firewall.
Add “%CUBRID%\bin\cub_broker.exe” to open all ports for cub_broker.
Add “%CUBRID%\bin\cub_cas.exe” to open all ports for CAS.
Add “%CUBRID%\bin\cub_master.exe” to open all ports for cub_master.
Add “%CUBRID%\bin\cub_server.exe” to open all ports for cub_server.
Add “%CUBRID%\bin\cub_cmserver.exe” to open all ports for the CUBRID Manager.
Add “%CUBRID%\bin\cub_javasp.exe” to open all ports for the CUBRID Java SP server.
If you use CUBRID for Linux at the broker machine or the DB server machine, all of Linux ports should be opened. If you use CUBRID for Windows at the broker machine or the DB server machine, all of Linux ports should be opened or the related processes should be added to the program list allowed for the Windows firewall.
Label |
Listener |
Requester |
Linux Port |
Windows Port |
Firewall Port Setting |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Default use |
cub_broker |
application |
BROKER_PORT |
BROKER_PORT |
Open |
One-time connection |
CAS |
application |
BROKER_PORT |
APPL_SERVER_PORT ~ (APP_SERVER_PORT + # of CAS - 1) |
Open |
Keep connected |
|
cub_master |
CAS |
cubrid_port_id |
cubrid_port_id |
Open |
One-time connection |
|
cub_server |
CAS |
cubrid_port_id |
A random available port |
Linux: Open Windows: Program |
Keep connected |
|
Client machine(*) |
cub_server |
ECHO(7) |
ECHO(7) |
Open |
Periodical connection |
|
Server machine(**) |
CAS, CSQL |
ECHO(7) |
ECHO(7) |
Open |
Periodical connection |
|
HA use |
cub_broker |
application |
BROKER_PORT |
Not supported |
Open |
One-time connection |
CAS |
application |
BROKER_PORT |
Not supported |
Open |
Keep connected |
|
cub_master |
CAS |
cubrid_port_id |
Not supported |
Open |
One-time connection |
|
cub_master (slave) |
cub_master (master) |
ha_port_id |
Not supported |
Open |
Periodical connection, check the heartbeat |
|
cub_master (master) |
cub_master (slave) |
ha_port_id |
Not supported |
Open |
Periodical connection, check the heartbeat |
|
cub_server |
CAS |
cubrid_port_id |
Not supported |
Open |
Keep connected |
|
Client machine(*) |
cub_server |
ECHO(7) |
Not supported |
Open |
Periodical connection |
|
Server machine(**) |
CAS, CSQL, copylogdb, applylogdb |
ECHO(7) |
Not supported |
Open |
Periodical connection |
|
Manager use |
Manager server |
application |
8001 |
8001 |
Open |
|
Java SP use |
cub_javasp |
cub_server |
java_stored_procedure_port |
java_stored_procedure_port |
Open |
Keep connected |
(*): The machine which has the CAS, CSQL, copylogdb, or applylogdb process
(**): The machine which has the cub_server
The detailed description on each classification is given as follows.
Default Ports for CUBRID
The following table summarizes the ports required for each OS, based on the listening processes. Each port on the listener should be opened.
Listener |
Requester |
Linux port |
Windows port |
Firewall Port Setting |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
cub_broker |
application |
BROKER_PORT |
BROKER_PORT |
Open |
One-time connection |
CAS |
application |
BROKER_PORT |
APPL_SERVER_PORT ~ (APP_SERVER_PORT + # of CAS - 1) |
Open |
Keep connected |
cub_master |
CAS |
cubrid_port_id |
cubrid_port_id |
Open |
One-time connection |
cub_server |
CAS |
cubrid_port_id |
A random available port |
Linux: Open Windows: Program |
Keep connected |
Client machine(*) |
cub_server |
ECHO(7) |
ECHO(7) |
Open |
Periodical connection |
Server machine(**) |
CAS, CSQL |
ECHO(7) |
ECHO(7) |
Open |
Periodical connection |
(*): The machine which has the CAS or CSQL process
(**): The machine which has the cub_server
Note
In Windows, you cannot specify the ports to open because CAS randomly specifies the ports as accessing the cub_server. In this case, add “%CUBRID%\bin\cub_server.exe” to “Windows Firewall > Allowed programs”.
As the server process (cub_server) and the client processes (CAS, CSQL) cross-check if the opposite node is normally running or not by using the ECHO(7) port, you should open the ECHO(7) port if there is a firewall. If the ECHO port cannot be opened for both the server and the client, set the check_peer_alive parameter value of the cubrid.conf to none.
The relation of connection between processes is as follows:
application - cub_broker
-> CAS - cub_master
-> cub_server
application: The application process
cub_broker: The broker server process. It selects CAS to connect with the application.
CAS: The broker application server process. It relays the application and the cub_server.
cub_master: The master process. It selects the cub_server to connect with the CAS.
cub_server: The database server process
The symbols of relation between processes and the meaning are as follows:
- : Indicates that the connection is made only once for the initial.
->, <- : Indicates that the connection is maintained. The right side of -> or the left side of <- is the party that the arrow symbol indicates. The party that the arrow symbol indicates is the listener which listens to the opposite process.
(master): Indicates the master node in the HA configuration.
(slave): Indicates the slave node in the HA configuration.
The connection process between the application and the DB is as follows:
The application tries to connect to the cub_broker through the broker port (BROKER_PORT) set in the cubrid_broker.conf.
The cub_broker selects a connectable CAS.
The application and CAS are connected.
In Linux, established TCP connection between the BROKER and the client will be passed to the CAS. Therefore, there is no need for an additional network port for the application to connect to the CAS. However, in Windows, when an application connects to a BROKER, the BROKER delivers the network port number to connect to the available CAS to the application. After the client closes the current connection with the BROKER, it connects to the CAS with the received network port number from the BROKER. If the APPL_SERVER_PORT parameter is not set, the network port used by the first CAS becomes BROKER_PORT + 1.
For example, if the BROKER_PORT is 33000 and the APPL_SERVER_PORT value has not been set in Windows, the ports used between the application and CAS are as follows:
The port used to connect the application to the CAS(1): 33001
The port used to connect the application to the CAS(2): 33002
The port used to connect the application to the CAS(3): 33003
CAS sends a request of connecting with the cub_server to the cub_master through the cubrid_port_id port set in the cubrid.conf.
CAS and the cub_server are connected.
In Linux, you should use the cubrid_port_id port as CAS is connected to the cub_server through the Unix domain socket. In Windows, CAS is connected to the cub_server through a random available port as the Unix domain socket cannot be used. If the DB server is running in Windows, a random available port is used between the broker machine and the DB server machine. In this case, note that the operation may not be successful if a firewall blocks the port for the process between the two machines.
After that, CAS keeps connection with the cub_server even if the application is terminated until the CAS restarts.
Ports for CUBRID HA
The CUBRID HA is supported in Linux only.
The following table summarizes the ports required for each OS, based on the listening processes. Each port on the listener should be opened.
Listener |
Requester |
Linux port |
Firewall Port Setting |
Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
cub_broker |
application |
BROKER_PORT |
Open |
One-time connection |
CAS |
application |
BROKER_PORT |
Open |
Keep connected |
cub_master |
CAS |
cubrid_port_id |
Open |
One-time connection |
cub_master (slave) |
cub_master (master) |
ha_port_id |
Open |
Periodical connection, check the heartbeat |
cub_master (master) |
cub_master (slave) |
ha_port_id |
Open |
Periodical connection, check the heartbeat |
cub_server |
CAS |
cubrid_port_id |
Open |
Keep connected |
Client machine(*) |
cub_server |
ECHO(7) |
Open |
Periodical connection |
Server machine(**) |
CAS, CSQL, copylogdb, applylogdb |
ECHO(7) |
Open |
Periodical connection |
(*): The machine which has the CAS, CSQL, copylogdb, or applylogdb process
(**): The machine which has the cub_server
As the server process (cub_server) and the client processes (CAS, CSQL, copylogdb, applylogdb, etc.) cross-check if the opposite node is normally running or not by using the ECHO(7) port, you should open the ECHO(7) port if there is a firewall. If the ECHO port cannot be opened for both the server and the client, set the ref:check_peer_alive <check_peer_alive> parameter value of the cubrid.conf to none.
The relation of connection between processes is as follows:
application - cub_broker
-> CAS - cub_master(master) <-> cub_master(slave)
-> cub_server(master) cub_server(slave) <- applylogdb(slave)
<----------------------- copylogdb(slave)
cub_master(master): the master process on the master node in the CUBRID HA configuration. It checks if the peer node is alive.
cub_master(slave): the master process on the slave node in the CUBRID HA configuration. It checks if the peer node is alive.
copylogdb(slave): the process which copies the replication log on the slave node in the CUBRID HA configuration
applylogdb(slave): the process which applies the replication log on the slave node in the CUBRID HA configuration
For easy understanding for the replication process from the master node to the slave node, the applylogdb and copylogdb on the master node and CAS on the slave node have been omitted.
The symbols of relation between processes and the meaning are as follows:
- : Indicates that the connection is made only once for the initial.
->, <- : Indicates that the connection is maintained. The right side of -> or the left side of <- is the party that the arrow symbol indicates. The party that the arrow symbol indicates is the listener which listens to the opposite process.
(master): Indicates the master node in the HA configuration.
(slave): Indicates the slave node in the HA configuration.
The connection process between the application and the DB is identical with Default Ports for CUBRID. This section describes the connection process between the master node and the slave node when the master DB and the slave DB are configured 1:1 by the CUBRID HA.
The ha_port_id set in the cubrid_ha.conf is used between the cub_master(master) and the cub_master(slave).
The copylogdb(slave) sends a request for connecting with the master DB to the cub_master(master) through the port set in the cubrid_port_id of the cubrid.conf on the slave node. Finally, the copylogdb(slave) is connected with the cub_server(master).
The applylogdb(slave) sends a request for connecting with the slave DB to the cub_master(slave) through the port set in the cubrid_port_id of the cubrid.conf on the slave node. Finally, the applylogdb(slave) is connected with the cub_server(slave).
On the master node, the applylogdb and the copylogdb run for the case that the master node is switched to the slave node.
Ports for CUBRID Manager Server
The following table summarizes the ports, based on the listening processes, used for CUBRID Manager server. The ports are identical regardless of the OS type.
Listener |
Requester |
Port |
Firewall Port Setting |
|---|---|---|---|
Manager server |
application |
8001 |
Open |
The port used when the CUBRID Manager client accesses the CUBRID Manager server process is cm_port of the cm.conf. The default value is 8001.
Ports for CUBRID Java Stored Procedure Server
The following table summarizes the ports, based on the listening processes, used for CUBRID Java Stored Procedure (Java SP) server. The ports are identical regardless of the OS type.
Listener |
Requester |
Port |
Firewall Port Setting |
|---|---|---|---|
cub_javasp |
cub_server |
java_stored_procedure_port |
Open |
The port used when the CUBRID Java stored procedure server (cub_javasp) to communicate with the cub_server is java_stored_procedure_port of the cubrid.conf. The default value of java_stored_procedure_port is 0, which means a random available port is assigned.